4 stages of competence in business development: This is stage 1 in the competency process, and there is no guarantee that someone.

Four Stages of Competence PowerPoint Template SketchBubble
The four stages of competence 1.
4 stages of competence. Then see if you can spot yourself among the four stages of competence listed below. In conscious incompetence, the learner is aware of a skill or knowledge gap and understands. You don’t know what you don’t know.
Later on we’ll also take a look at how they can help you and your clients avoid frustration and disappointment when learning a new skill or changing a behavior. When you first learn how. The competency has now become embedded in the dna of the organisation.
Recognize their own incompetence, and see value in the new skill. The four stages of competence can be summarised as follows: The person feels no need to acquire that particular skill, and does not realize the fact that he will not be able to.
In unconscious incompetence, the learner isn’t aware that a skill or knowledge gap exists. Tying your shoes and unconscious. ‘i know what i don’t know’.
One of my favorite examples is learning how to drive. Truly dedicated language learners eventually reach the fourth stage of learning, the summit of “unconscious competence.” you can now communicate effortlessly in the language, saying what you want to say, and understanding almost everything you hear or read. It may be broken down into steps, and there is heavy conscious involvement in executing the new skill.
‘i grow and improve and that slowly shows’. The third stage of the four stages of competency is conscious competence. This is the stage where you don’t know what you don’t know.
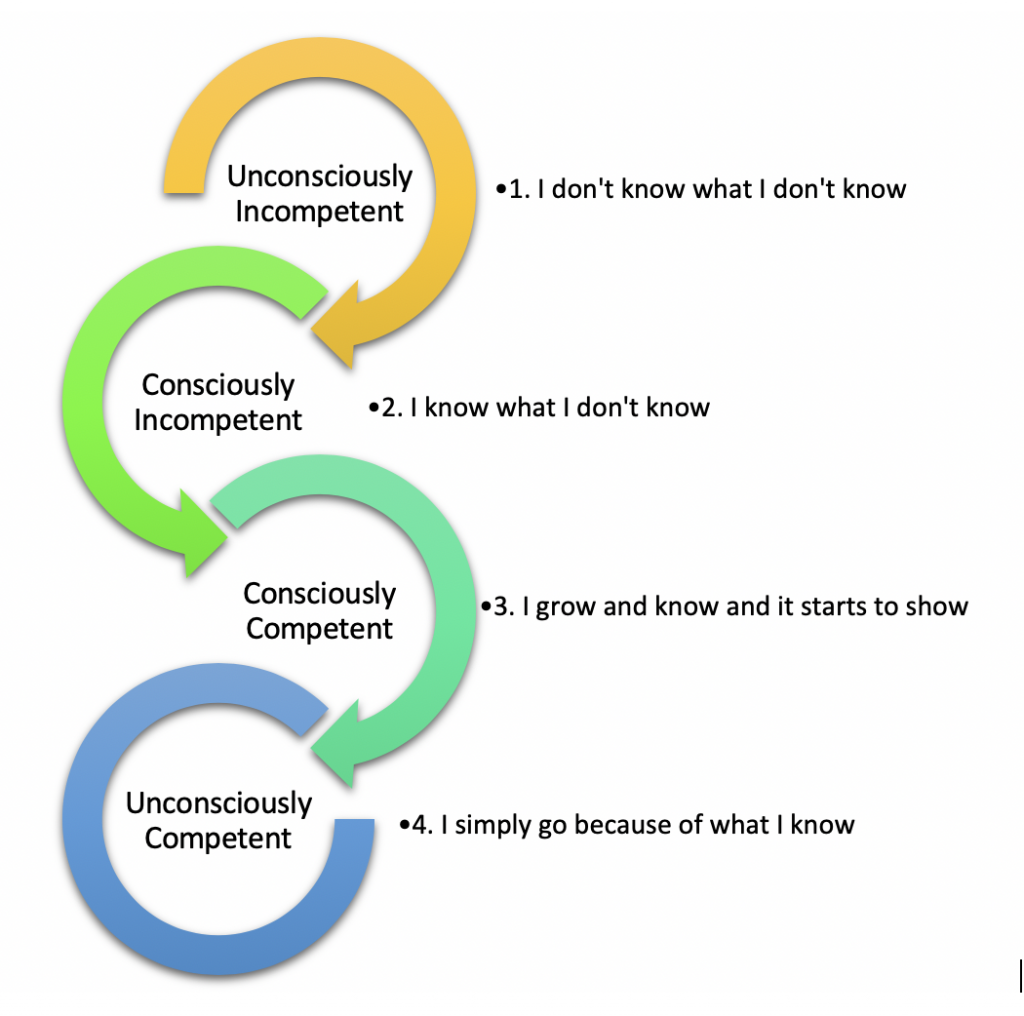
There are four stages of developing competence: Aware of the skill and proficient with effort. In psychology, the four stages of competence, or the “conscious competence” learning model, relates to the psychological states involved in the process of progressing from incompetence to competence in a skill.
However, demonstrating the skill or knowledge requires concentration. This is where we finally reach the point where we’re able to produce work that sounds great, but we’re really aware of every move that we’re making. To move on to the second stage the learner has to do two things;
Unconscious incompetence — this is the phase where you don’t know what you don’t know. This is the level native speakers operate in when. Perhaps you can think of times when you have driven to work and you barely remember which route you.
The 4 stages of competence stage one: Here are the 4 stages of competence according to burch’s original model. Knowing these 4 stages of competence has moved me forward at times when i’ve felt incredibly frustrated that i’m not making enough progress.
Since he is unaware of the skill, he does not know about its utility and relevance. Think about how many times you’ve driven home or to a familiar location without thought for where to turn, when to switch lanes to get to your exit, etc. Conscious competence (learning) the individual understands or knows how to do something.
It’s helped me to see that progress comes out of feeling incompetent! Strategy and operations follow the methodology and an optimal level of process. The 4 stages of competence this simple model simply states that each individual must pass through four different stages when learning a new skill.
Driving a car and unconscious competence. To be unconsciously incompetent is to be unaware of a personal deficit. Understanding the 4 stages of competence.
This stage is summed up by the. Final thoughts on the four stages of learning. The four stages of competence 1.
Thus, you recognize your weak points and understand the importance of acquiring new knowledge. As an individual, you do not understand or know how to do. In this stage, a person is unaware of the existence of a particular skill.
The first one is the one that offended me right out of the gate. A coach will be able to see the learners' deficit and guide them through the learning process, it’s the. You perform the task without thought.
I have so much competence that i don’t need to know (unconscious process competence) this is the ultimate stage of process competence. Conscious incompetence (awareness) though the individual does not understand or know how to do something, he or she. ‘i don’t know what i don’t know’.
One tactic that you can use is a paradigm of performance which is called the 4 stages of competence (also known as the 4 stages of learning). The four stages of competence. The making of mistakes can be integral to the learning process at this stage.[4] 3.
The four stages of competence model has a number of different interpretations but typically suggests that there are four stages to learning any new skill: The four stages of competence. The think about how good you are at performing the behavior.
We’re intellectualizing every decision that we’re making. Conscious incompetence is the second stage of competence. How to use this information to develop skills and talents.
We’re thinking a lot about every choice. This is the stage where you’re starting to realize that there are things you don’t know. Aware of the skill but lacking proficiency.
Initially described as “four stages for learning any new skill”, the four stages of learning provides a model for learning. 4 stages of competence from unconscious incompetence to unconscious competence. Unconscious incompetence (ignorance) the individual does not understand or know how to do something and does not.
You are lack knowledge and skills in the area in question and are unaware of this lack. It’s the beginning of the learning curve where you aren’t even aware of how little you know.

FROM UNCONSCIOUS TO UNCONSCIOUS COMPETENCE Download
We may feel safe, secure and experience moderate success.
Unconscious incompetence to unconscious competence. It can be a really useful way of thinking about the human element of business processes and there’s a significant body of knowledge that uses the model as a way of thinking about. It may be a simple intuitive feeling or a failure. In this state, where you can exist for a very long time, you are not as competent as one or more of:
The “you don't know what you don't know” or “you only know what you know”. As they recognize their incompetence, they consciously acquire a skill, then consciously use it. Dealing with unconscious incompetent people — growth | people | results.
This ability paves the way for the learning of new skills in people. This could result in trainees leaving us in a state of unconscious incompetence. In unconscious incompetence, the learner isn’t aware that a skill or knowledge gap exists.
We don't know what we don't know so may not even be bothered by this lack of knowledge. This condition relates to the room dominated by. If you only do two things to help people achieve unconscious competence:
This stage is summed up by the phrase: Then, something happens to shake us up. The individual is said to have then acquired unconscious competence.
Conscious competence theory of learning a new skill credited to: In this phase, a ‘master’ can influence other persons to develop unconscious incompetence. Simply put, this is when you don’t know what you don’t know.
In conscious incompetence, the learner is aware of a skill or knowledge gap and understands. You have to help others move through these four stages—from unconscious incompetence to unconscious competence—and guide them with clarity and. It’s the time before you learned how to do a skill and before you were aware that you needed to learn that skill.
The “whole is greater than the parts”. These stages can be used to explain the rationale behind decisions or actions and is as such pretty useful in a business. In other words, before we begin to gain a new skill, we are unaware of our.
“it's automatic” or you “see and feel” the possibilities and the outcome. The phase of the conscious leaning model are described below: Senior consultants may be interested to.
Gordon training international by its employee noel burch in the 1970s most of us start here: But that’s what you have to do. Unconscious incompetence for some, this is the ignorance is bliss stage.
Relate, a british relationship counseling service, relies on volunteer counselors. The four stages of competence 1. The four stages suggest that individuals are initially unaware of how little they know, or unconscious of their incompetence.
“i don’t know what i don’t know.”. Worryingly, proposals for foundation year 2 will result in many shos spending only 4 months working within our speciality. Conscious incompetence though the individual does not understand or know how to do something, he or she does recognize.
This is probably where you hope to be — you are aware that you need to improve. Ask people if they are missing any resources they need to implement their training. Eventually, the skill can be utilized without it being consciously thought through:
Consciousness (awareness) and skill level (competence). They receive extensive initial training and continuous assessment, passing through stages from incompetence to the point at which competence becomes unconscious. Conscious competence of unconscious incompetence;
Quite often, on treading new territory, 'unconscious incompetence' becomes perceptible, namely what we cannot do, or do not know. Noel burch, an employee with gordon training international, developed the conscious competence ladder in the 1970s. While this is not included in burch’s original model, many experts are campaigning for the inclusion of this fifth stage.
Allow time and opportunity for people to build up new skills and habits gradually, giving them plenty of time for practice. As a thought leader, you understand your subject so instinctively and deeply that it may be difficult for you to explain it at the content’s most basic level. As an unconscious incompetent, you do not know what you do not know.
The four stages of competence 1. According to the model, we move through the following levels as we build competence in a. We’ve all seen people like.
This is that point when things. Unconscious incompetence (ignorance) the individual does not understand or know how to do something and does not necessarily recognize the deficit. But we should remember that this should not be the end of the learning journey but the begining, until they have reached the stage of unconscious competence.
The two states of conscious incompetence are distinguished by improvements in knowledge and skills. We move from unconscious incompetence to conscious incompetence to conscious competence and finally to unconscious competence. Then as they work their way through the learning, you might have different activities to test the various levels of competency, hence strengthening the learning.
The model highlights two factors that affect our thinking as we learn a new skill: Unconscious incompetence the individual does not understand or know how to do something and does not necessarily. The psychology of human development deals with four stages of competence, ranging from unconscious incompetence to unconscious competence.
Watch my video on creating conscious competence.
-
An online marketing plan that includes mobile publicity. Pr firms use some business directories, online platforms, social media, publication...
-
Crossing fingers might be one of the most complex gestures invented by humanity. Thumbs up means ok in america but in iran it has the same e...
-
If i improve sales by 15% i can get a promotion. This will help to focus on the strengths, minimize weaknesses and take the greatest possibl...
watch your six
Watch Your Six Meaning, Origin & Example. . When used in combat scenarios, “watch your six” literally means “keep an eye on what’s...

ads
